Discover expert tips for a healthier heart. Explore lifestyle changes, diet, and exercises to improve heart health and boost overall well-being.
Maintaining optimal heart health is imperative for overall well-being, as the heart plays a central role in sustaining life. To enhance heart health, adopting a multifaceted approach is essential. Firstly, cultivating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, sodium, and added sugars is crucial. Regular physical activity, encompassing both aerobic exercises and strength training, contributes significantly to cardiovascular fitness. Additionally, managing stress through practices such as meditation or deep breathing exercises is pivotal, as chronic stress can adversely affect heart health. Abstaining from tobacco products and moderating alcohol intake are key lifestyle adjustments to further support cardiovascular well-being. Routine check-ups and monitoring key indicators like blood pressure and cholesterol levels also aid in early detection and management of potential issues. By incorporating these lifestyle modifications, individuals can proactively work towards improving and sustaining heart health, fostering a foundation for a longer and healthier life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various lifestyle changes and habits that can significantly contribute to improving heart health.
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet:
Adopting a heart-healthy diet is paramount in the pursuit of improving heart health, as dietary choices play a pivotal role in influencing cardiovascular well-being. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall heart health. These foods are inherently low in saturated and trans fats, helping to maintain healthy cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. Furthermore, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids from sources such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts can positively impact cholesterol profiles and promote heart health.
Limiting the intake of sodium is crucial in managing blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease. High sodium consumption can lead to hypertension, increasing the strain on the heart. By choosing fresh, minimally processed foods and using herbs and spices for flavoring instead of salt, individuals can effectively control their sodium intake. Additionally, adopting a heart-healthy diet involves minimizing the consumption of added sugars, which have been linked to obesity, diabetes, and other risk factors for heart disease.
In essence, a heart-healthy diet serves as a cornerstone for cardiovascular well-being by fostering optimal cholesterol levels, regulating blood pressure, and mitigating other risk factors associated with heart disease. By making mindful and nutritious food choices, individuals can significantly contribute to the improvement and maintenance of their heart health, promoting longevity and overall wellness.
A balanced and nutritious diet is a cornerstone of heart health.
Focus on incorporating the following elements into your meals:
-
- a. Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a colorful variety to ensure a diverse range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- b. Whole Grains: Choose whole grains over refined grains for higher fiber content, which aids in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
- c. Lean Proteins: Opt for lean sources of protein, such as fish, poultry, beans, and legumes, while limiting red meat intake.
- d. Healthy Fats: Include sources of unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, while minimizing saturated and trans fats.
Monitor and Manage Cholesterol Levels:
Monitoring and managing cholesterol levels is paramount for improving heart health due to the direct and substantial impact of cholesterol on cardiovascular well-being. Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance crucial for building cell membranes and producing hormones. However, an imbalance in cholesterol levels, particularly elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, poses a significant risk to heart health. LDL cholesterol can accumulate in the walls of arteries, forming plaque that narrows and obstructs blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis, a major precursor to heart disease.
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels through lipid profile blood tests is essential for early detection of imbalances. This enables individuals to intervene promptly through lifestyle modifications or medication if necessary. Managing cholesterol involves maintaining a delicate balance between LDL and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “good” cholesterol. HDL cholesterol helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of plaque formation.
Effective management of cholesterol levels typically involves adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe cholesterol-lowering medications to control levels more effectively. By proactively monitoring and managing cholesterol levels, individuals can mitigate the risk of atherosclerosis, lower the likelihood of heart disease, and ultimately enhance overall cardiovascular health, contributing to a longer and healthier life.
High cholesterol is a significant risk factor for heart disease.
Regularly check your cholesterol levels and take steps to manage them effectively:
-
- a. Limit Saturated Fats: Reduce intake of foods high in saturated fats, such as fatty meats and full-fat dairy products.
- b. Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Consume fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, known to lower cholesterol.
- c. Choose Plant Sterols: Foods fortified with plant sterols can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol.

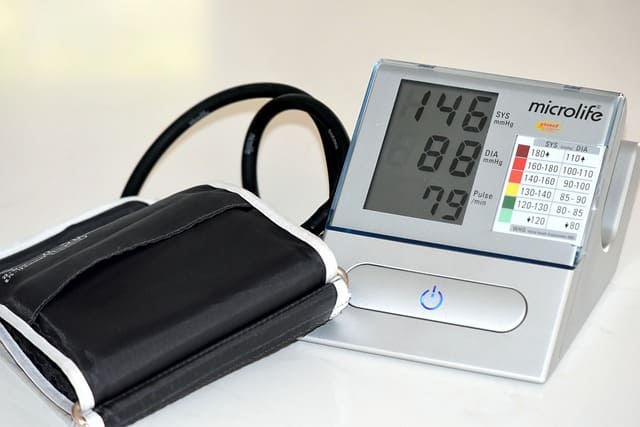
Maintain a Healthy Blood Pressure:
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is of paramount importance in improving heart health due to its direct influence on the overall cardiovascular system. Blood pressure is the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries, and its regulation is essential for the proper functioning of the heart and circulation. The significance of maintaining healthy blood pressure lies in its role as a critical determinant of the strain on the heart and the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Consistently high blood pressure, or hypertension, can lead to the thickening and narrowing of arteries, making the heart work harder to pump blood. This increased workload may contribute to the development of conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and stroke. Additionally, hypertension is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, further escalating the risk of heart-related complications.
Regular monitoring and maintenance of blood pressure within a healthy range (typically around 120/80 mmHg) are essential for preventing the long-term adverse effects on the heart and blood vessels. Lifestyle modifications, including a heart-healthy diet low in sodium, regular physical activity, weight management, and limiting alcohol intake, play a pivotal role in blood pressure control. In cases of persistent hypertension, healthcare providers may recommend medications to help regulate blood pressure effectively.
By prioritizing the maintenance of a healthy blood pressure, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, enhance the efficiency of the heart’s pumping function, and promote overall heart health. This proactive approach contributes to a longer, more vibrant life with a decreased likelihood of heart-related complications.
Hypertension is a leading cause of heart disease.
Adopt these practices to keep your blood pressure in check:
-
- a. Reduce Sodium Intake: Limit processed foods and opt for fresh, whole foods to lower sodium intake.
- b. Exercise Regularly: Engage in physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, to help manage blood pressure.
- c. Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises into your routine.
Stay Physically Active:
Staying physically active is crucial for improving heart health, as regular exercise confers a multitude of benefits that directly contribute to the overall well-being of the cardiovascular system. Engaging in physical activity enhances the efficiency of the heart and promotes better circulation, leading to a range of positive outcomes. Firstly, exercise plays a pivotal role in managing and maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity—a significant risk factor for heart disease. Additionally, regular physical activity helps control blood pressure by improving the flexibility and health of blood vessels, reducing the strain on the heart and minimizing the risk of hypertension.
Furthermore, exercise positively influences lipid profiles by raising levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “good” cholesterol, and lowering levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol. This balance is crucial in preventing the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, mitigating the risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. Physical activity also contributes to better glucose control, reducing the incidence of diabetes—a condition closely linked to heart disease.
Regular exercise fosters overall cardiovascular endurance and enhances the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently. It improves oxygen utilization, boosts energy levels, and reduces stress, all of which are integral to heart health. Moreover, exercise promotes the release of endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators, and contributes to mental well-being, indirectly benefiting heart health by reducing stress and anxiety.
Individuals can incorporate physical activity into their routine through various forms, including aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming, as well as strength training. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, complemented by muscle-strengthening activities at least two days per week.
In summary, staying physically active is a cornerstone of improving heart health, offering a holistic approach to cardiovascular well-being. By integrating regular exercise into daily life, individuals not only enhance their heart’s functionality but also address multiple risk factors associated with heart disease, ultimately fostering a healthier and more resilient cardiovascular system.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Maintaining a healthy weight is a critical factor in improving heart health, as excess body weight, especially when concentrated around the abdominal area, significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Obesity is associated with a range of detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, and addressing weight-related issues offers numerous benefits for heart health. Firstly, achieving and sustaining a healthy weight helps regulate blood pressure, reducing the strain on the heart and lowering the risk of hypertension—a major contributor to heart disease.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also closely linked to optimal lipid profiles. Excess body weight, particularly visceral fat, is associated with elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides, while simultaneously reducing levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. This imbalance contributes to the formation of arterial plaque and increases the risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. By attaining a healthy weight, individuals can positively influence their lipid profiles, mitigating these risks and promoting better heart health.
Furthermore, obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes, which in turn elevates the risk of heart disease. Maintaining a healthy weight helps regulate blood glucose levels, reducing the likelihood of insulin resistance and diabetes-related complications. Weight management also improves the overall function of the cardiovascular system, enhancing the heart’s efficiency in pumping blood and reducing the workload on the entire circulatory system.
Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, combined with regular physical activity, forms the foundation for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. The combination of a calorie-controlled diet and regular exercise not only aids in weight loss but also contributes to overall cardiovascular fitness. Additionally, lifestyle modifications that promote healthier eating habits and increased physical activity can be sustainable, offering long-term benefits for both weight management and heart health.
Quit Smoking:
Quitting smoking is paramount for improving heart health, as tobacco use is a major modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Smoking not only damages the heart and blood vessels directly but also contributes to the development of atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke accelerate the formation of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and heightened blood pressure. Moreover, smoking diminishes the levels of beneficial high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and raises levels of detrimental low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, exacerbating the risk of coronary artery disease. Quitting smoking promptly results in immediate cardiovascular benefits, including improved blood circulation, lowered heart rate, and a reduced risk of blood clot formation. Long-term cessation significantly diminishes the likelihood of heart disease, emphasizing the pivotal role of smoking cessation in enhancing heart health and overall well-being.
The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke accelerate the formation of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and heightened blood pressure. Moreover, smoking diminishes the levels of beneficial high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and raises levels of detrimental low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, exacerbating the risk of coronary artery disease. Quitting smoking promptly results in immediate cardiovascular benefits, including improved blood circulation, lowered heart rate, and a reduced risk of blood clot formation. Long-term cessation significantly diminishes the likelihood of heart disease, emphasizing the pivotal role of smoking cessation in enhancing heart health and overall well-being.
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Limiting alcohol consumption is crucial for improving heart health, as excessive and chronic alcohol intake has been linked to various cardiovascular issues. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some cardiovascular benefits, excessive drinking poses significant risks, including high blood pressure, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmias. Consuming alcohol in excess can elevate blood pressure, weaken the heart muscle, and disrupt the normal rhythm of the heart. Moreover, excessive alcohol intake contributes to the accumulation of visceral fat, raising the risk of obesity and associated heart-related complications. By moderating alcohol consumption, individuals can help maintain a healthy weight, regulate blood pressure, and reduce the overall strain on the cardiovascular system. Practicing moderation in alcohol consumption is a key aspect of a heart-healthy lifestyle, promoting better cardiovascular outcomes and mitigating potential risks associated with excessive drinking.
Moreover, excessive alcohol intake contributes to the accumulation of visceral fat, raising the risk of obesity and associated heart-related complications. By moderating alcohol consumption, individuals can help maintain a healthy weight, regulate blood pressure, and reduce the overall strain on the cardiovascular system. Practicing moderation in alcohol consumption is a key aspect of a heart-healthy lifestyle, promoting better cardiovascular outcomes and mitigating potential risks associated with excessive drinking.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, enhancing heart health requires a comprehensive and proactive approach that encompasses various lifestyle modifications. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, while minimizing saturated fats and sugars, lays the foundation for optimal cardiovascular well-being. Regular physical activity is paramount, not only for weight management but also for improving blood circulation, controlling blood pressure, and optimizing lipid profiles. Monitoring and managing cholesterol levels, staying physically active, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption collectively contribute to a robust strategy for improving heart health. By prioritizing these lifestyle changes, individuals can mitigate risk factors associated with cardiovascular diseases, promote better overall well-being, and pave the way for a longer, healthier life. Regular medical check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals further empower individuals to personalize their approach, ensuring a tailored and effective journey towards lasting heart health.
Remember, taking care of your heart is an ongoing journey. By prioritizing a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and routine monitoring, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease and set yourself up for a healthy and vibrant life.
FAQs about Improving Heart Health:
Q: What should I eat for a healthy heart?
A: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limit saturated and trans fats, sugar, and processed foods.
Q: How much exercise is enough?
A: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise. Don’t forget strength training and incorporating activity into daily life.
Q: Can stress hurt my heart?
A: Absolutely! Manage stress through yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or spending time in nature. Uncontrolled stress can raise blood pressure and increase heart disease risk.
Q: What are the main risk factors for heart disease?
A: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and family history are key risk factors. Knowing your numbers and managing them is crucial.
Q: How often should I check my blood pressure and cholesterol?
A: Follow your doctor’s recommendations, but generally, annual checks are advised. Regular monitoring helps identify and address potential issues early.
Q: What other lifestyle changes can improve heart health?
A: Get enough sleep, quit smoking, limit alcohol intake, and control weight. These small changes collectively make a big difference for your heart.
Q: Can supplements help protect my heart?
A: Talk to your doctor before taking any supplements. While some like omega-3 fatty acids may offer benefits, a balanced diet and exercise are the cornerstones of good heart health.
Q: What resources can help me improve my heart health?
A: The American Heart Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and registered dietitians offer valuable information, recipes, and personalized guidance.
Q: Does technology play a role?
A: Wearable devices and fitness trackers can help you monitor activity, sleep, and stress levels, motivating you to make healthy choices for your heart.
Q: How can I make small, sustainable changes for my heart?
A: Start with one or two things you can easily incorporate into your daily routine, like taking the stairs or swapping a sugary drink for water. Small steps consistently taken add up to big improvements over time.
Q: Is it ever too late to improve heart health?
A: Absolutely not! No matter your age or current health status, making positive changes can always benefit your heart and overall well-being.